Publications
Selected Papers
[NDSS’25][ Distinguished Paper Award ] Provably Unlearnable Data Examples (Paper | Code)
Derui Wang, Minhui Xue, Bo Li, Seyit Camtepe, Liming Zhu
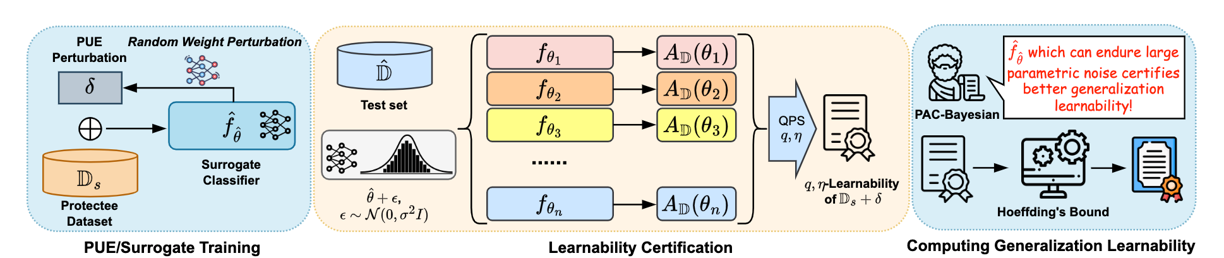
We introduce the theory of certified learnability in this paper. Certified $(q,\eta)$-Learnability measures how learnable a dataset is by computing a probabilistic upper bound on the test performance of classifiers trained on this dataset, as long as those classifiers fall within a certified parameter set. We use certified $(q,\eta)$-Learnability as a measurement of the effectiveness and robustness of unlearnable examples, and propose Provably Unlearnable Examples (PUEs) which can lead to reduced $(q,\eta)$-Learnability when training classifiers on them.
[USENIX Security’25] CAMP in the Odyssey: Provably Robust Reinforcement Learning with Certified Radius Maximization (Paper | Code)
Derui Wang, Kristen Moore, Diksha Goel, Minjune Kim, Gang Li, Yang Li, Robin Doss, Minhui Xue, Bo Li, Seyit Camtepe, Liming Zhu
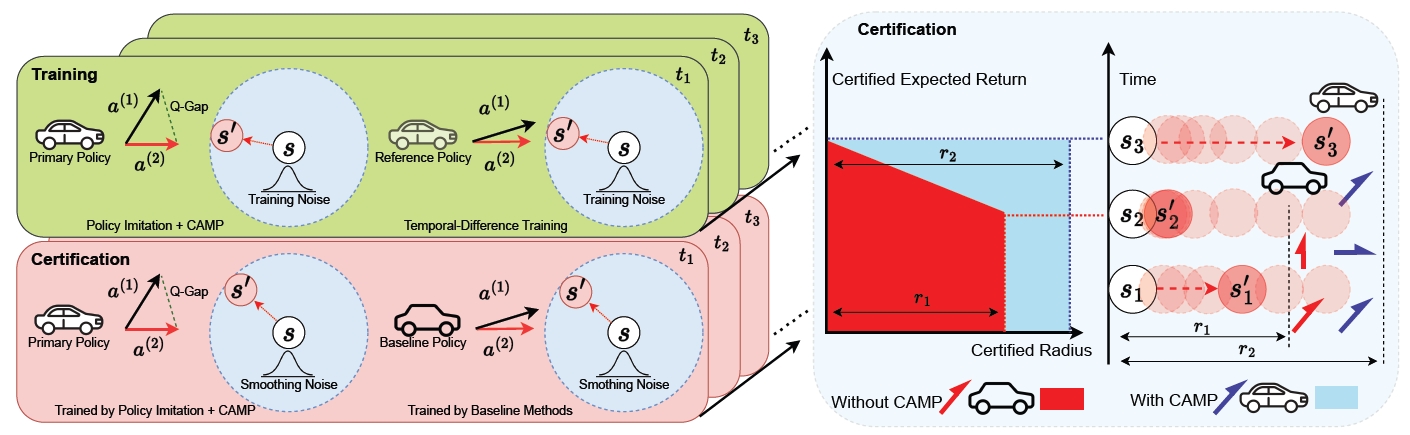
We introduce a novel paradigm dubbed {C}ertified-r{A}dius-{M}aximizing {P}olicy (CAMP) training for certifiably robust deep reinforcement learning (DRL) agents. CAMP is designed to enhance DRL policies, achieving better utility without compromising provable robustness. By leveraging the insight that the global certified radius can be derived from local certified radii based on training-time statistics, CAMP formulates a surrogate loss related to the local certified radius and optimizes the policy guided by this surrogate loss. We also introduce policy imitation as a novel technique to stabilize CAMP training. Experimental results demonstrate that CAMP significantly improves the robustness-return trade-off across various tasks. Based on the results, CAMP can achieve up to twice the certified expected return compared to that of baselines. Our code is also available at Zenodo.
[ICML’24] Effects of Exponential Gaussian Distribution on (Double Sampling) Randomized Smoothing (Paper | Code)
Youwei Shu, Xi Xiao, Derui Wang, Yuxin Cao, Siji Chen, Minhui Xue, Linyi Li, Bo Li
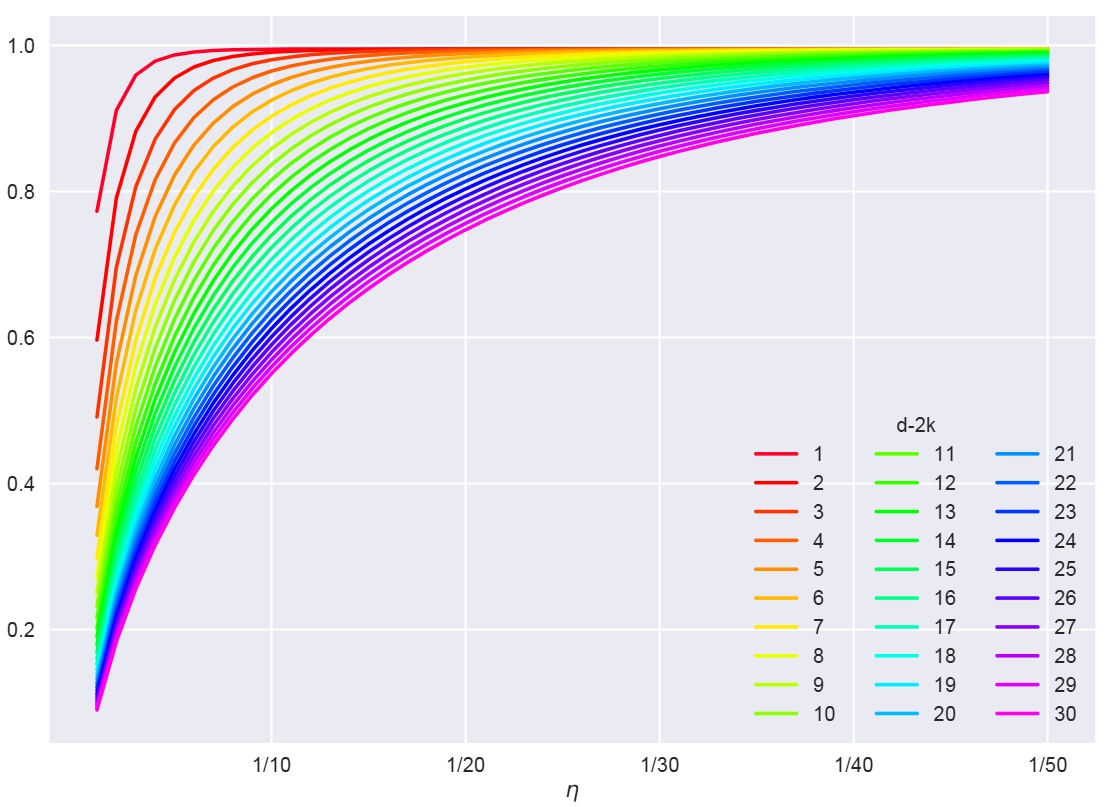
We address in this paper the curse of dimensionality of Randomized Smoothing (RS). RS is currently a scalable certified defense method providing robustness certification against adversarial examples. Although significant progress has been achieved in providing defenses against $\ell_p$ adversaries, the interaction between the smoothing distribution and the robustness certification still remains vague. In this work, we comprehensively study the effect of two families of distributions, named Exponential Standard Gaussian (ESG) and Exponential General Gaussian (EGG) distributions, on Randomized Smoothing and Double Sampling Randomized Smoothing (DSRS). We derive an analytic formula for ESG’s certified radius, which converges to the origin formula of RS as the dimension $d$ increases. Additionally, we prove that EGG can provide tighter constant factors than DSRS in providing $\Omega(\sqrt{d})$ lower bounds of $\ell_2$ certified radius, and thus further addresses the curse of dimensionality in RS. Compared to the primitive DSRS, the increase in certified accuracy provided by EGG is prominent, up to 6.4% on ImageNet.
[USENIX Security’25] SafeSpeech: Robust and Universal Voice Protection Against Malicious Speech Synthesis (Paper | Code)
Zhisheng Zhang, Derui Wang, Qianyi Yang, Pengyang Huang, Junhan Pu, Yuxin Cao, Kai Ye, Jie Hao
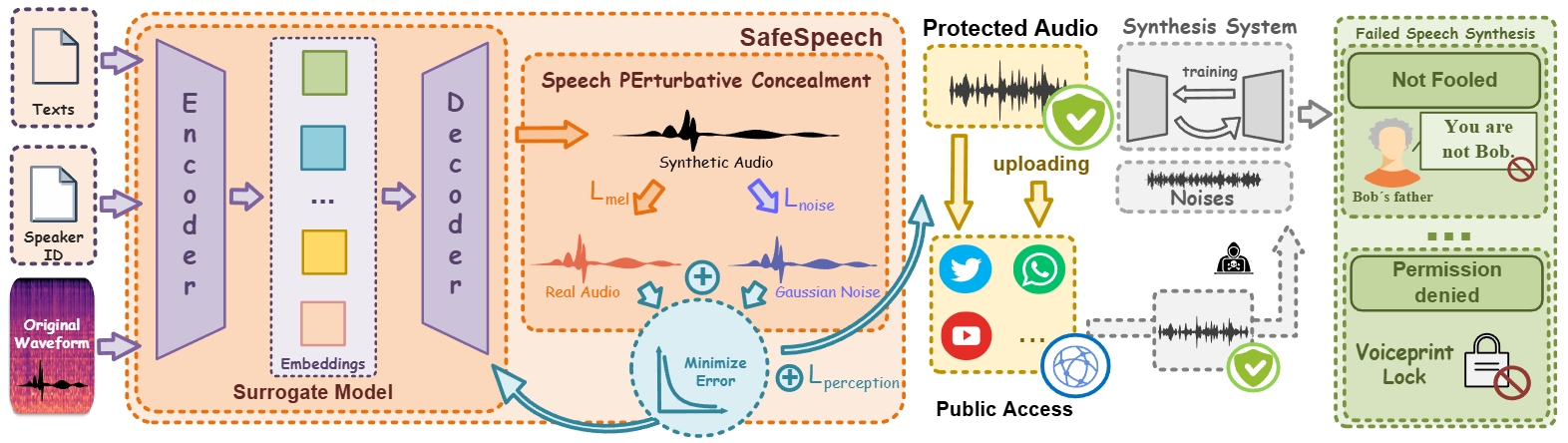
Speech synthesis technology has brought significant convenience, but the widespread use of realistic deepfake audio has also introduced considerable hazards. In particular, models trained on large-scale speech corpora can now generate highly realistic audio. By fine-tuning pretrained models, attackers require only a few minutes of speech samples to synthesize high-quality speeches with realistic timbre, rhythm, and phonemes. For example, criminals have used deepfake speech to impersonate a German executive, tricking a British subsidiary head into transferring $243,000.
In response, we introduce SafeSpeech, a method designed to protect users’ audio prior to publication by embedding imperceptible perturbations into the original speeches, thereby preventing the synthesis of high-quality deepfake audio. SafeSpeech achieves SOTA voice protection effectiveness and transferability and is highly robust against advanced adaptive adversaries. Importantly, in real-world tests, SafeSpeech demonstrated real-time capability by providing continuous protection for streaming audio data after a 14-second warmup.
[NDSS’23] The “Beatrix’’ Resurrections: Robust Backdoor Detection via Gram Matrices (Paper | Code)
Wanlun Ma, Derui Wang, Ruoxi Sun, Minhui Xue, Sheng Wen, Yang Xiang
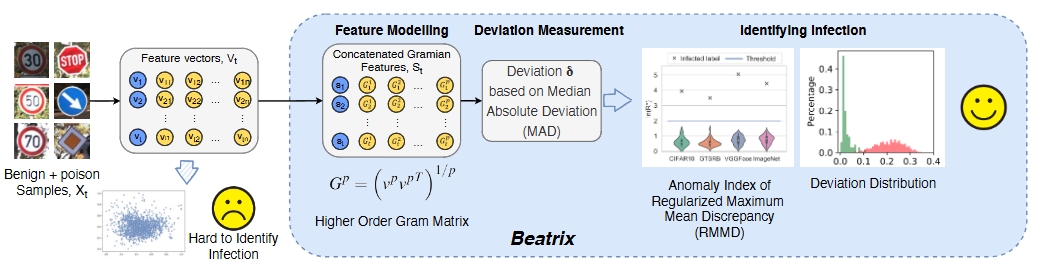
We propose Beatrix (backdoor detection via Gram matrix) as an effective detector against dynamic backdoors. Beatrix utilizes Gram matrix to capture not only the feature correlations but also the appropriately high-order information of the representations. By learning class-conditional statistics from activation patterns of normal samples, Beatrix can identify poisoned samples by capturing the anomalies in activation patterns. To further improve the performance in identifying target labels, Beatrix leverages kernel-based testing without making any prior assumptions on representation distribution. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method through extensive evaluation and comparison with state-of-the-art defensive techniques. The experimental results show that our approach achieves an F1 score of 91.1% in detecting dynamic backdoors, while the state of the art can only reach 36.9%.
[SP’23] StyleFool: Fooling Video Classification Systems via Style Transfer (Paper | Code)
Yuxin Cao, Xi Xiao, Ruoxi Sun, Derui Wang, Minhui Xue, Sheng Wen
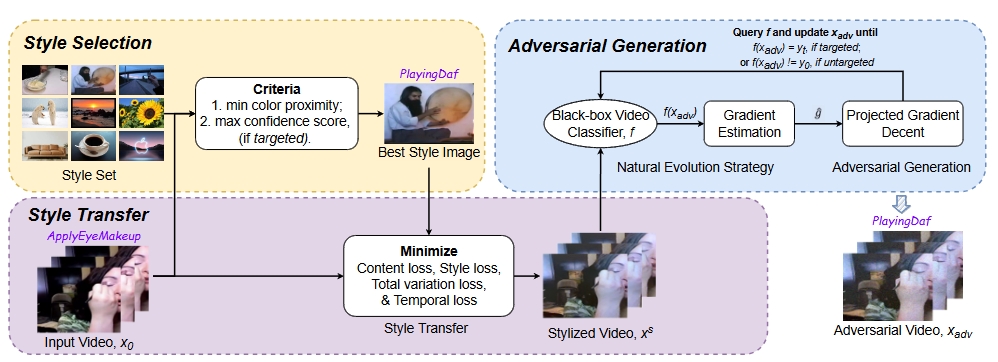
Video classification systems are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, which can create severe security problems in video verification. Current black-box attacks need a large number of queries to succeed, resulting in high computational overhead in the process of attack. On the other hand, attacks with restricted perturbations are ineffective against defenses such as denoising or adversarial training. We proposed StyleFool in this paper a gradient-free red-teaming method to evaluate the robustness of video classification systems. Leveraging style-transfer, our perturbations are crafted to be more indistinguishable for human auditors. Moreover, StyleFool outperforms the state-of-the-art adversarial attacks in terms of both the number of queries and the robustness against existing defenses.
List of Publications
The list of my publications can also be found on my Google Scholar. * marks a corresponding author, if specified.
[1] Luyu Zhu, Kai Ye, Jiayu Yao, Chenxi Li, Luwen Zhao, Yuxin Cao, Derui Wang, and Jie Hao. Maid: Model attribution via inverse diffusion. In International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2025.
[2] Zhisheng Zhang, Derui Wang, Qianyi Yang, Pengyang Huang, Junhan Pu, Yuxin Cao, Kai Ye, Jie Hao, and Yixian Yang. Safespeech: Robust and universal voice protection against malicious speech synthesis. In USENIX Security Symposium, 2025.
[3] Dayong Ye, Tianqing Zhu, Congcong Zhu, Derui Wang, Zewei Shi, Sheng Shen, Wanlei Zhou, and Minhui Xue. Reinforcement unlearning. In Network and Distributed System Security (NDSS) Symposium, 2025.
[4] Zihan Wang, Zhongkui Ma, Xinguo Feng, Zhiyang Mei, Ethan Ma, Derui Wang, Minhui Xue, and Guangdong Bai. Ai model modulation with logits redistribution. In The ACM Web Conference (WWW), 2025.
[5] Yamei Wang, Yuexin Zhang, Ayong Ye, Jian Shen, Derui Wang, and Yang Xiang. Anonymous and efficient $(t,n)$-threshold ownership transfer for cloud emrs auditing. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2025.
[6] Derui Wang, Minhui Xue, Bo Li, Seyit Camtepe, and Liming Zhu. Provably unlearnable data examples. In Network and Distributed System Security (NDSS) Symposium, 2025 ( Distinguished Paper Award ).
[7] Derui Wang, Kristen Moore, Diksha Goel, Minjune Kim, Gang Li, Yang Li, Robin Doss, Minhui Xue, Bo Li, Seyit Camtepe, and Liming Zhu. Camp in the odyssey: Provably robust reinforcement learning with certified radius maximization. In USENIX Security Symposium, 2025.
[8] Minjune Kim, Jeff Wang, Kristen Moore, Diksha Goel, Derui Wang, Ahmad Mohsin, Ahmed Ibrahim, Robin Doss, Seyit Camtepe, and Helge Janicke. Cyberally: Leveraging llms and knowledge graphs to empower cyber defenders. In Companion Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference (WWW Companion), 2025.
[9] Weifei Jin, Yuxin Cao, Junjie Su, Derui Wang, Yedi Zhang, Minhui Xue, Jie Hao, Jin Song Dong, and Yixian Yang. Whispering under the eaves: Protecting user privacy against commercial and llm-powered automatic speech recognition systems. In USENIX Security Symposium, 2025.
[10] Mingming Gong, Yiliao Song, Yun Sing Koh, Wei Xiang, and Derui Wang. Ai 2024: Advances in artificial intelligence, 2025.
[11] Huajie Chen, Tianqing Zhu, Lefeng Zhang, Bo Liu, Derui Wang, Wanlei Zhou, and Minhui Xue. Queen: Query unlearning against model extraction. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2025.
[12] Yuxin Cao, Kai Ye, Derui Wang, Minhui Xue, Hao Ge, Chenxiong Qian, and Jin Song Dong. Bones of contention: Exploring query-efficient attacks against skeleton recognition systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.16843, 2025.
[13] Zhisheng Zhang, Qianyi Yang, Derui Wang, Pengyang Huang, Yuxin Cao, Kai Ye, and Jie Hao. Mitigating unauthorized speech synthesis for voice protection. In CCS-LAMPS, 2024.
[14] Duoxun Tang, Yuxin Cao, Xi Xiao, Derui Wang, Sheng Wen, and Tianqing Zhu. Query-efficient video adversarial attack with stylized logo. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.12099, 2024.
[15] Youwei Shu, Xi Xiao, Derui Wang, Yuxin Cao, Siji Chen, Jason Xue, Linyi Li, and Bo Li. Effects of exponential gaussian distribution on (double sampling) randomized smoothing. In International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2024.
[16] Wanlun Ma, Derui Wang, Chao Chen, Sheng Wen, Gaolei Fei, and Yang Xiang. Locguard: A location privacy defender for image sharing. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2024.
[17] Weifei Jin, Yuxin Cao, Junjie Su, Qi Shen, Kai Ye, Derui Wang, Jie Hao, and Ziyao Liu. Towards evaluating the robustness of automatic speech recognition systems via audio style transfer. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM Workshop on Secure and Trustworthy Deep Learning Systems, pages 47–55, 2024.
[18] Diksha Goel, Kristen Moore, Mingyu Guo, Derui Wang, Minjune Kim, and Seyit Camtepe. Optimizing cyber defense in dynamic active directories through reinforcement learning. In European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, pages 332–352, 2024.
[19] Yuxin Cao, Yumeng Zhu, Derui Wang, Sheng Wen, Minhui Xue, Jin Lu, and Hao Ge. Rethinking the threat and accessibility of adversarial attacks against face recognition systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.08514, 2024.
[20] Yuxin Cao, Jinghao Li, Xi Xiao, Derui Wang, Minhui Xue, Hao Ge, Wei Liu, and Guangwu Hu. Localstylefool: Regional video style transfer attack using segment anything model. In IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops (SPW), 2024.
[21] Wanlun Ma, Derui Wang, Ruoxi Sun, Minhui Xue, Sheng Wen, and Yang Xiang. The “beatrix” resurrections: Robust backdoor detection via gram matrices. In The Network and Distributed System Security (NDSS) Symposium, 2023.
[22] Yuxin Cao, Ziyu Zhao, Xi Xiao, Derui Wang, Minhui Xue, and Jin Lu. Logostylefool: Vitiating video recognition systems via logo style transfer. In The 38th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2023.
[23] Yuxin Cao, Xi Xiao, Ruoxi Sun, Derui Wang, Minhui Xue, and Sheng Wen. Stylefool: Fooling video classification systems via style transfer. In IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), 2023.
[24] Yuxin Cao, Yian Li, Yumeng Zhu, Derui Wang*, and Minhui Xue*. Flow-attention-based spatio-temporal aggregation network for 3d mask detection. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2023.
[25] Derui Wang, Sheng Wen, Alireza Jolfaei, Mohammad Sayad Haghighi, Surya Nepal, and Yang Xiang. On the neural backdoor of federated generative models in edge computing. ACM Transactions on Internet Technology, 22(2):1–21, 2021.
[26] Derui Wang, Chaoran Li, Sheng Wen, Qing-Long Han, Surya Nepal, Xiangyu Zhang, and Yang Xiang. Daedalus: Breaking non-maximum suppression in object detection via adversarial examples. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 52(8):7427–7440, 2021.
[27] Chaoran Li, Xiao Chen, Derui Wang, Sheng Wen, Muhammad Ejaz Ahmed, Seyit Camtepe, and Yang Xiang. Backdoor attack on machine learning based android malware detectors. IEEE Transactions on dependable and secure computing, 19(5):3357–3370, 2021.
[28] Derui Wang, Chaoran Li, Sheng Wen, Surya Nepal, and Yang Xiang. Man-in-the-middle attacks against machine learning classifiers via malicious generative models. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 18(5):2074–2087, 2020.
[29] Derui Wang, Chaoran Li, Sheng Wen, Surya Nepal, and Yang Xiang. Defending against adversarial attack towards deep neural networks via collaborative multi-task training. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 19(2):953–965, 2020.
[30] Yansong Gao, Change Xu, Derui Wang, Shiping Chen, Damith C Ranasinghe, and Surya Nepal. Strip: A defence against trojan attacks on deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference (ACSAC), pages 113–125, 2019.
[31] Xiao Chen, Chaoran Li, Derui Wang, Sheng Wen, Jun Zhang, Surya Nepal, Yang Xiang, and Kui Ren. Android hiv: A study of repackaging malware for evading machine-learning detection. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 15:987–1001, 2019.
[32] Derek Wang, Wanlei Zhou, James Xi Zheng, Sheng Wen, Jun Zhang, and Yang Xiang. Who spread to whom? inferring online social networks with user features. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), pages 1–6. IEEE, 2018.
[33] Tingmin Wu, Derek Wang, Sheng Wen, and Yang Xiang. How spam features change in twitter and the impact to machine learning based detection. In Information Security Practice and Experience (ISPEC), 2017.
[34] Derek Wang, Tingmin Wu, Sheng Wen, Xiaofeng Chen, Yang Xiang, and Wanlei Zhou. Stc: exposing hidden compromised devices in networked sustainable green smart computing platforms by partial observation. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Computing, 4(2):178–190, 2017.
[35] Derek Wang, Sheng Wen, Yang Xiang, Wanlei Zhou, Jun Zhang, and Surya Nepal. Catch me if you can: detecting compromised users through partial observation on networks. In 2017 IEEE 37th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), pages 2417–2422. IEEE, 2017.
[36] Derui Wang and Jingyu Hou. Explore the hidden treasure in protein–protein interaction networks—an iterative model for predicting protein functions. Journal of bioinformatics and computational biology, 13(05):1550026, 2015.
